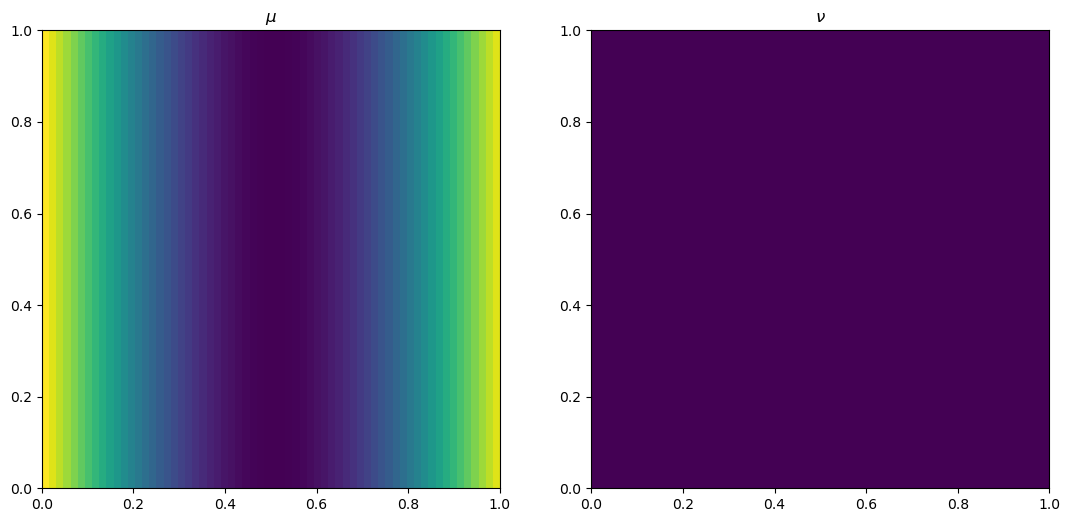
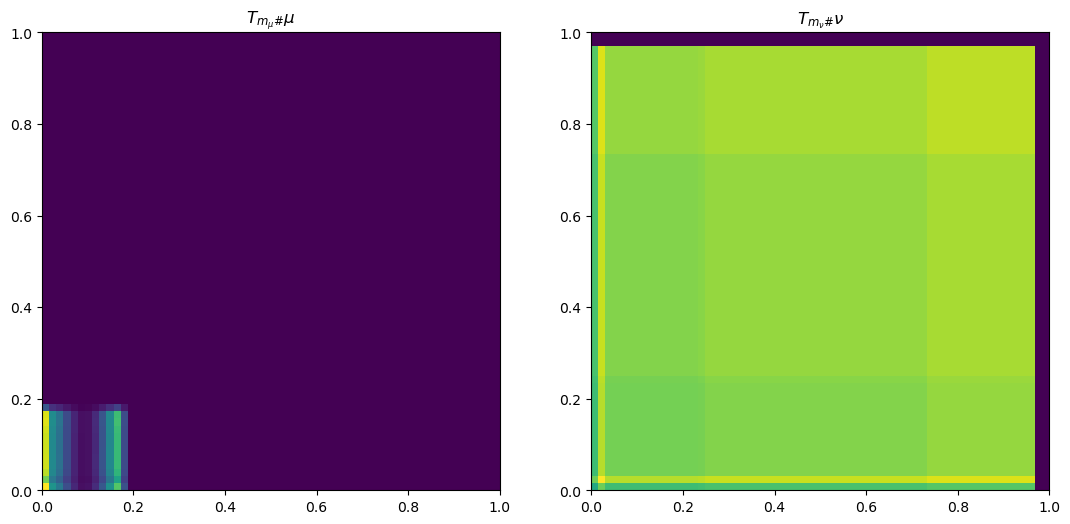
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (13, 8)
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'viridis'
# Function definitions
def initialize_kernel(n1, n2):
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(0, np.pi, n1, False), np.linspace(0, np.pi, n2, False))
kernel = 2 * n1 * n1 * (1 - np.cos(xx)) + 2 * n2 * n2 * (1 - np.cos(yy))
kernel[0, 0] = 1 # to avoid dividing by zero
return kernel
def dct2(a):
#discrete cosine transform
return dctn(a, norm='ortho')
def idct2(a):
#inverse discrete cosine transform
return idctn(a, norm='ortho')
def update_potential(phi, rho, nu, kernel, sigma):
n1, n2 = nu.shape
rho -= nu
workspace = dct2(rho) / kernel
workspace[0, 0] = 0
workspace = idct2(workspace)
phi += sigma * workspace
h1 = np.sum(workspace * rho) / (n1 * n2)
return h1
def compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y):
n1, n2 = mu.shape
return np.sum(0.5 * (x * x + y * y) * (mu + nu) - nu * phi.reshape((n1, n2)) - mu * psi.reshape((n1, n2))) / (n1 * n2)
def compute_w2_wop(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y, m_mu, m_nu):
n1, n2 = mu.shape
return np.sum(0.5 * (x * x + y * y) * (mu + nu) - nu * phi.reshape((n1, n2)) - mu * psi.reshape((n1, n2)) + (m_mu - m_nu) ** 2) / (n1 * n2)
def stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq):
scaleDown = 0.95
scaleUp = 1 / scaleDown
upper = 0.75
lower = 0.25
diff = value - oldValue
if diff > gradSq * sigma * upper:
return sigma * scaleUp
elif diff < gradSq * sigma * lower:
return sigma * scaleDown
return sigma
# use the pudhforward function in the c file
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def compute_ot(phi, psi, bf, sigma):
kernel = initialize_kernel(n2, n1)
rho = np.copy(mu)
oldValue = compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y)
for k in range(numIters + 1):
# Perform gradient and potential updates
gradSq = update_potential(phi, rho, nu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
value = compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y)
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
bf.pushforward(rho, phi, nu)
# Update potential and push forward for psi
gradSq = update_potential(psi, rho, mu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
bf.pushforward(rho, psi, mu)
# Logging the values
if k % 10 == 0:
print(f'iter {k:4d}, W2 value: {value:.6e}, H1 err: {gradSq:.2e}')
#if k % 10 == 0:
#print(bf.xMap, bf.yMap)
# Update stepsize and oldValue for next iteration
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
def compute_ot_wop(phi, psi, bf, sigma):
kernel = initialize_kernel(n2, n1)
rho = np.copy(mu)
oldValue = compute_w2_wop(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y, m_mu, m_nu)
for k in range(numIters + 1):
# Perform gradient and potential updates
gradSq = update_potential(phi, rho, nu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
value = compute_w2_wop(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y, m_mu, m_nu)
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
bf.pushforward(rho, phi, nu)
# Update potential and push forward for psi
gradSq = update_potential(psi, rho, mu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
bf.pushforward(rho, psi, mu)
# Logging the values
if k % 10 == 0:
print(f'iter {k:4d}, W2 value: {value:.6e}, H1 err: {gradSq:.2e}')
#if k % 10 == 0:
#print(bf.xMap, bf.yMap)
# Update stepsize and oldValue for next iteration
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
# functions for calculating the pushforward by mass
import numpy as np
from scipy.signal import convolve2d
def sampling_pushforward_jit(rho, xMap, yMap, mu, n1, n2, totalMass):
"""
Compute the pushforward measure using a sampling-based method.
Parameters:
rho (np.ndarray): Array of shape (n1, n2) to store the resulting density.
xMap (np.ndarray): The computed x-coordinate mapping (shape must be (n1+1, n2+1)).
yMap (np.ndarray): The computed y-coordinate mapping (shape must be (n1+1, n2+1)).
mu (np.ndarray): Source measure (density) of shape (n1, n2).
n1 (int): Number of grid points in the x-direction.
n2 (int): Number of grid points in the y-direction.
totalMass (float): The total mass to normalize the output density.
"""
# 1) Clear out rho
pcount = n1 * n2
for i in range(n1):
for j in range(n2):
rho[i, j] = 0.0
# 2) Loop over each cell and subdivide
for i in range(n1):
for j in range(n2):
mass = mu[i, j]
if mass > 0.0:
# Compute stretches along x and y
xStretch0 = abs(xMap[i, j+1] - xMap[i, j])
xStretch1 = abs(xMap[i + 1, j+1] - xMap[i + 1, j])
yStretch0 = abs(yMap[i + 1, j] - yMap[i, j])
yStretch1 = abs(yMap[i + 1, j+1] - yMap[i, j+1])
xStretch = max(xStretch0, xStretch1)
yStretch = max(yStretch0, yStretch1)
xSamples = max(int(n1 * xStretch), 1)
ySamples = max(int(n2 * yStretch), 1)
factor = 1.0 / (xSamples * ySamples)
# 3) Sample within the cell
for l in range(ySamples):
b = (l + 0.5) / ySamples
for k in range(xSamples):
a = (k + 0.5) / xSamples
# Bilinear interpolation for xMap and yMap
xPoint = (
(1 - b)*(1 - a)*xMap[i, j] +
(1 - b)*a *xMap[i, j+1] +
b *(1 - a)*xMap[i + 1, j] +
a*b *xMap[i + 1, j+1]
)
yPoint = (
(1 - b)*(1 - a)*yMap[i, j] +
(1 - b)*a *yMap[i, j+1] +
b *(1 - a)*yMap[i + 1, j] +
a*b *yMap[i + 1, j+1]
)
# Convert continuous coordinates to discrete indices
X = xPoint * n1 - 0.5
Y = yPoint * n2 - 0.5
xIndex = int(X)
yIndex = int(Y)
xFrac = X - xIndex
yFrac = Y - yIndex
xOther = xIndex + 1
yOther = yIndex + 1
# Clamp indices
xIndex = max(0, min(xIndex, n1-1))
xOther = max(0, min(xOther, n1-1))
yIndex = max(0, min(yIndex, n2-1))
yOther = max(0, min(yOther, n2-1))
# 4) Distribute mass using bilinear weights
w00 = (1.0 - xFrac)*(1.0 - yFrac)
w01 = (1.0 - xFrac)*yFrac
w10 = xFrac*(1.0 - yFrac)
w11 = xFrac*yFrac
rho[yIndex, xIndex] += w00 * mass * factor
rho[yOther, xIndex] += w01 * mass * factor
rho[yIndex, xOther] += w10 * mass * factor
rho[yOther, xOther] += w11 * mass * factor
# 5) Normalize so that the total measure equals totalMass
sum_rho = 0.0
for i in range(n1):
for j in range(n2):
sum_rho += rho[i, j]
sum_rho /= pcount # average density
if sum_rho > 0.0:
scale = totalMass / sum_rho
for i in range(n1):
for j in range(n2):
rho[i, j] *= scale
def cal_pushforward_map(dual, n1, n2):
"""
Compute the pushforward map (xMap and yMap) from the dual variable.
Parameters:
dual (np.ndarray): The dual variable (often denoted phi).
n1 (int): Number of grid points in the x-direction.
n2 (int): Number of grid points in the y-direction.
Returns:
xMap (np.ndarray), yMap (np.ndarray): The computed mapping arrays.
"""
kernel = np.array([[0.25, 0.25],
[0.25, 0.25]])
dual_padded = np.pad(dual, ((1, 1), (1, 1)), mode="edge")
interpolate_function = convolve2d(dual_padded, kernel, mode="valid")
interpolate_function_padded = np.pad(interpolate_function, ((1, 1), (1, 1)), mode="edge")
xMap = 0.5 * n2 * (interpolate_function_padded[1:-1, 2:] - interpolate_function_padded[1:-1, :-2])
yMap = 0.5 * n1 * (interpolate_function_padded[2:, 1:-1] - interpolate_function_padded[:-2, 1:-1])
return xMap, yMap
def pushforward_mass(phi, nu, n1, n2):
"""
Perform the pushforward of the measure 'nu' using the dual variable 'phi',
and store the resulting measure in 'rho'.
Parameters:
rho (np.ndarray): An (n1 x n2) array to store the pushforward measure.
phi (np.ndarray): The dual variable used to compute the pushforward map.
nu (np.ndarray): The source measure (density) on the grid.
n1 (int): Number of grid points in the x-direction.
n2 (int): Number of grid points in the y-direction.
totalMass (float): The total mass for normalization.
Returns:
np.ndarray: The updated pushforward measure stored in 'rho'.
"""
rho = np.zeros((n1, n2))
totalMass = np.sum(nu) / (n1 * n2)
# Compute the pushforward maps based on phi
xMap, yMap = cal_pushforward_map(phi, n1, n2)
# Use the sampling pushforward method to update rho
sampling_pushforward_jit(rho, xMap, yMap, nu, n1, n2, totalMass)
return rho
def plot_interpolation_wop(mu, nu, phi, psi, bf, x, y, n1, n2, m_mu, m_nu, n_fig=6):
"""
Plots the discrete geodesic interpolation between mu and nu
using the given potentials phi and psi.
Parameters
----------
mu : 2D array (n2, n1)
Source measure.
nu : 2D array (n2, n1)
Target measure.
phi, psi : 2D arrays (n2, n1)
Kantorovich potentials.
bf : BFM object
Instance of the Semi-discrete solver that has a pushforward method.
x, y : 2D arrays (n2, n1)
Grid coordinates.
n_fig : int
Number of frames to plot (including t=0 and t=1).
"""
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, n_fig, figsize=(20, 8))
for axi in ax:
axi.axis('off')
# Use the same max for color scaling
vmax = mu.max()
# Allocate arrays for intermediate pushforwards
interpolate = np.zeros_like(mu)
rho_fwd = np.zeros_like(mu)
rho_bwd = np.zeros_like(mu)
# "Reference" potential = 0.5*(x² + y²)
phi_0 = 0.5 * (x**2 + y**2)
# Generate intermediate frames
for i in range(0, n_fig):
# t = (1 - np.cos(math.pi * i / (n_fig - 1))) / 2
t_star = i / (n_fig - 1)
t = t_star / ((m_mu / m_nu) + t_star * (1 - m_mu / m_nu))
# Blend potentials in 2D form
# psi_t interpolates from phi_0 to psi
# phi_t interpolates from phi_0 to phi
psi_t = (1 - t) * phi_0 + t * psi
phi_t = t * phi_0 + (1 - t) * phi
m_t = (1 - t) * m_mu + t * m_nu
# Pushforward mu by psi_t
bf.pushforward(rho_fwd, psi_t, mu)
# Pushforward nu by phi_t
bf.pushforward(rho_bwd, phi_t, nu)
# reverse the oushforwards by mass
phi_mu_re = 0.5 * ((1/m_t) * (x * x) + (1/m_t) * y * y)
phi_nu_re = 0.5 * ((m_mu) * (x * x) + (m_mu) * y * y)
rho_fwd = pushforward_mass(phi_mu_re, rho_fwd, n1, n2)
rho_bwd = pushforward_mass(phi_nu_re, rho_bwd, n1, n2)
# Convex combination of the two pushforwards
interpolate = rho_fwd * m_t
# Plot the interpolation
ax[i].imshow(interpolate, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), vmax=vmax)
ax[i].set_title(f"$t={t:.2f}$")