Another Illustration of the Back-and-Forth Method#
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath("../.."))
import numpy as np
import numpy.ma as ma
from scipy.fftpack import dctn, idctn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from time import time
from BFOT.BFOT import BFM
from skimage.transform import resize
from skimage.filters import unsharp_mask
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[1], line 10
8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
9 from time import time
---> 10 from BFOT.BFOT import BFM
11 from skimage.transform import resize
12 from skimage.filters import unsharp_mask
File ~/work/BFOT/BFOT/BFOT/BFOT.py:2
1 import numpy as np
----> 2 import numba
3 from numba import prange
4 from scipy.signal import convolve2d
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numba'
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (13, 8)
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'viridis'
# Function definitions
def initialize_kernel(n1, n2):
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(0, np.pi, n1, False), np.linspace(0, np.pi, n2, False))
kernel = 2 * n1 * n1 * (1 - np.cos(xx)) + 2 * n2 * n2 * (1 - np.cos(yy))
kernel[0, 0] = 1 # to avoid dividing by zero
return kernel
def dct2(a):
return dctn(a, norm='ortho')
def idct2(a):
return idctn(a, norm='ortho')
def update_potential(phi, rho, nu, kernel, sigma):
n1, n2 = nu.shape
# rho -= nu.flatten()
rho -= nu
# workspace = dct2(rho.reshape(n2, n1)) / kernel
workspace = dct2(rho) / kernel
workspace[0, 0] = 0
# workspace = idct2(workspace).flatten()
workspace = idct2(workspace)
phi += sigma * workspace
h1 = np.sum(workspace * rho) / (n1 * n2)
return h1
def compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y):
n1, n2 = mu.shape
return np.sum(0.5 * (x * x + y * y) * (mu + nu) - nu * phi.reshape((n1, n2)) - mu * psi.reshape((n1, n2))) / (n1 * n2)
scaleDown = 0.95
scaleUp = 1 / scaleDown
upper = 0.75
lower = 0.25
def stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq):
diff = value - oldValue
if diff > gradSq * sigma * upper:
return sigma * scaleUp
elif diff < gradSq * sigma * lower:
return sigma * scaleDown
return sigma
def compute_ot(phi, psi, bf, sigma):
kernel = initialize_kernel(n1, n2)
# rho = np.copy(mu.flatten())
rho = np.copy(mu)
oldValue = compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y)
for k in range(numIters + 1):
gradSq = update_potential(phi, rho, nu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
value = compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y)
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
# bf.pushforward(rho, phi, nu.flatten())
bf.pushforward(rho, phi, nu)
gradSq = update_potential(psi, rho, mu, kernel, sigma)
bf.ctransform(phi, psi)
bf.ctransform(psi, phi)
# bf.pushforward(rho, psi, mu.flatten())
bf.pushforward(rho, psi, mu)
value = compute_w2(phi, psi, mu, nu, x, y)
sigma = stepsize_update(sigma, value, oldValue, gradSq)
oldValue = value
if k % 5 == 0:
print(f'iter {k:4d}, W2 value: {value:.6e}, H1 err: {gradSq:.2e}')
def process_image(image_array, output_size, sharpen=False, sharpen_radius=1.0, sharpen_amount=1.5):
"""
Processes an image to a specified resolution and optionally applies sharpening.
Parameters:
image_array (np.ndarray): Input image as a NumPy array.
output_size (tuple): Desired output size as (height, width).
sharpen (bool): Whether to apply sharpening to the resized image. Default is False.
sharpen_radius (float): Radius for the unsharp mask filter. Default is 1.0.
sharpen_amount (float): Amount for the unsharp mask filter. Default is 1.5.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Processed image array.
"""
# Ensure input is a NumPy array
if not isinstance(image_array, np.ndarray):
raise ValueError("The input image must be a NumPy array.")
# Resize the image
resized_image = resize(image_array, output_size, anti_aliasing=True)
# Apply sharpening if requested
if sharpen:
processed_image = unsharp_mask(resized_image, radius=sharpen_radius, amount=sharpen_amount)
else:
processed_image = resized_image
return processed_image
Read from data, black is large pixel#
mu = 1-plt.imread('../../images/star.png')[:, :, 2]
nu = 1-plt.imread('../../images/fivestar.png')[:, :, 2]
# Grid of size n1 x n2
output_dim = (256,256)
numIters = 40
mu = process_image(mu,output_dim,sharpen=True)
nu = process_image(nu,output_dim,sharpen=True)
n1, n2 = mu.shape
print('[n1,n2]=',[n1,n2])
x, y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(0.5 / n1, 1 - 0.5 / n1, n1), np.linspace(0.5 / n2, 1 - 0.5 / n2, n2))
# phi = 0.5 * (x * x + y * y).flatten()
# psi = 0.5 * (x * x + y * y).flatten()
phi = 0.5 * (x * x + y * y)
psi = 0.5 * (x * x + y * y)
#-----------------#
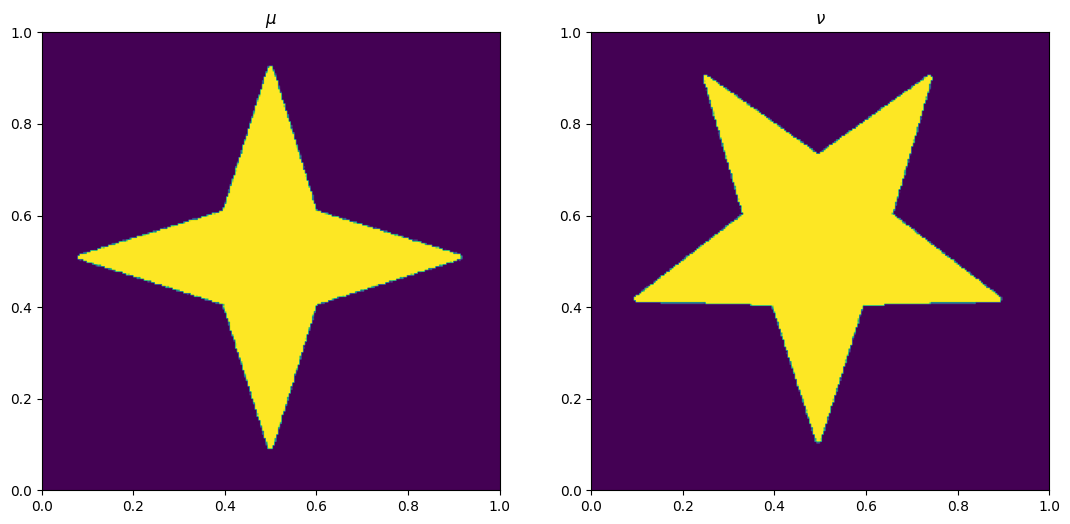
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax[0].imshow(mu, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1))
ax[0].set_title("$\\mu$")
ax[1].imshow(nu, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1))
ax[1].set_title("$\\nu$")
sigma = 4 / np.maximum(mu.max(), nu.max())
[n1,n2]= [256, 256]
tic = time()
bf = BFM(n1, n2, mu)
compute_ot(phi, psi, bf, sigma)
toc = time()
print(f'\nElapsed time: {toc - tic:.2f}s')
iter 0, W2 value: 1.336392e-04, H1 err: 4.73e-04
iter 5, W2 value: 1.330798e-03, H1 err: 3.46e-04
iter 10, W2 value: 2.123883e-03, H1 err: 1.22e-04
iter 15, W2 value: 2.636634e-03, H1 err: 5.47e-05
iter 20, W2 value: 3.051958e-03, H1 err: 5.48e-05
iter 25, W2 value: 3.466675e-03, H1 err: 5.48e-05
iter 30, W2 value: 3.881153e-03, H1 err: 5.48e-05
iter 35, W2 value: 4.295614e-03, H1 err: 5.48e-05
iter 40, W2 value: 4.710060e-03, H1 err: 5.48e-05
Elapsed time: 13.39s
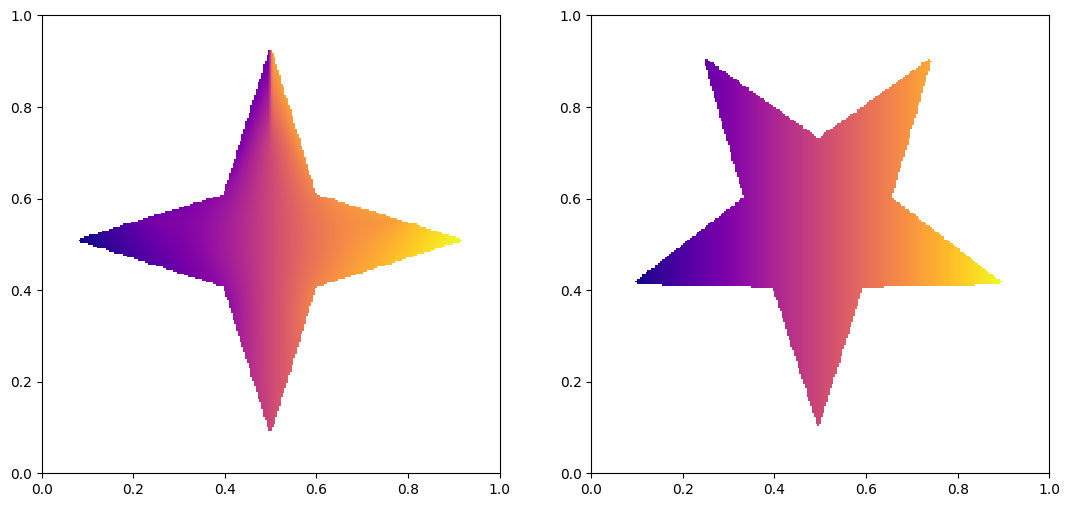
Lets plot the source and target image.
my, mx = ma.masked_array(np.gradient(psi.reshape((n2, n1)) - 0.5 * (x * x + y * y), 1 / n2, 1 / n1), mask=((mu == 0), (mu == 0)))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax[0].imshow((x + mx).reshape((n2, n1)), origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), cmap='plasma')
x_masked = ma.masked_array(x, mask=(nu == 0))
ax[1].imshow(x_masked, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), cmap='plasma')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x17cefcbe0>
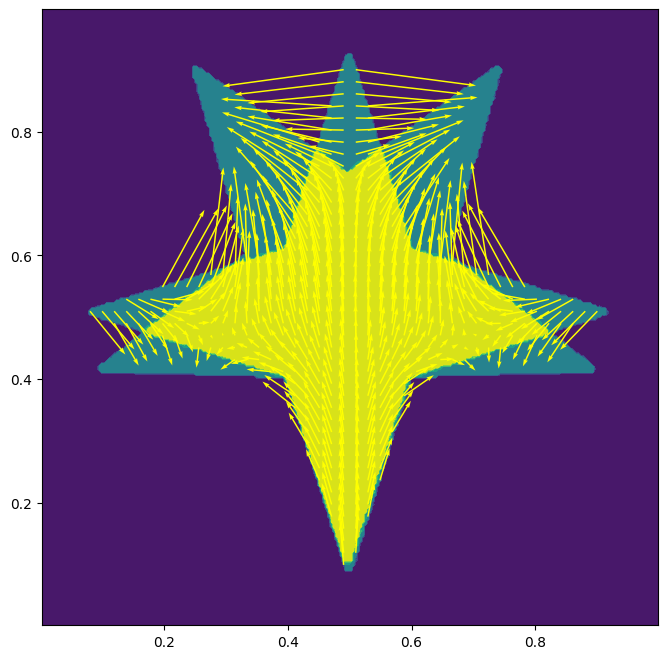
Now we draw the transformation.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.contourf(x, y, mu + nu)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
skip = (slice(None, None, n1 // 50), slice(None, None, n2 // 50))
ax.quiver(x[skip], y[skip], mx[skip], my[skip], color='yellow', angles='xy', scale_units='xy', scale=1)
<matplotlib.quiver.Quiver at 0x17d08fe20>
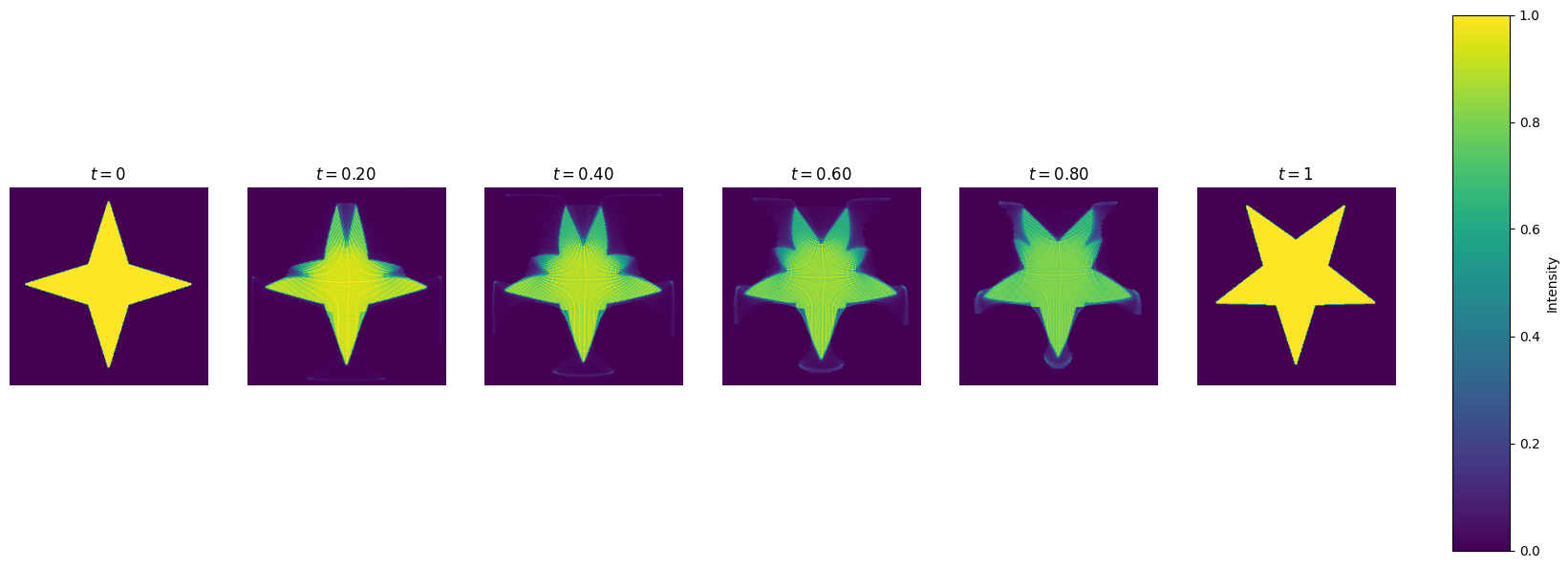
Let’s draw the snapshots of the transformation.
def plot_interpolation(mu, nu, phi, psi, bf, x, y, n_fig=6):
"""
Plots the discrete geodesic interpolation between mu and nu
using the given potentials phi and psi.
Parameters
----------
mu : 2D array (n2, n1)
Source measure.
nu : 2D array (n2, n1)
Target measure.
phi, psi : 2D arrays (n2, n1)
Kantorovich potentials.
bf : BFM object
Instance of the Semi-discrete solver that has a pushforward method.
x, y : 2D arrays (n2, n1)
Grid coordinates.
n_fig : int
Number of frames to plot (including t=0 and t=1).
"""
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, n_fig, figsize=(20, 8))
for axi in ax:
axi.axis('off')
# Use the same max for color scaling
vmax = max(mu.max(), nu.max())
# Show the initial and final measures
im0 = ax[0].imshow(mu, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), vmax=vmax)
ax[0].set_title("$t=0$")
ax[n_fig - 1].imshow(nu, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), vmax=vmax)
ax[n_fig - 1].set_title("$t=1$")
# Allocate arrays for intermediate pushforwards
interpolate = np.zeros_like(mu)
rho_fwd = np.zeros_like(mu)
rho_bwd = np.zeros_like(mu)
# "Reference" potential = 0.5*(x² + y²)
phi_0 = 0.5 * (x**2 + y**2)
# Generate intermediate frames
for i in range(1, n_fig - 1):
t = i / (n_fig - 1)
# Blend potentials in 2D form
# psi_t interpolates from phi_0 to psi
# phi_t interpolates from phi_0 to phi
psi_t = (1 - t) * phi_0 + t * psi
phi_t = t * phi_0 + (1 - t) * phi
# Pushforward mu by psi_t
bf.pushforward(rho_fwd, psi_t, mu)
# Pushforward nu by phi_t
bf.pushforward(rho_bwd, phi_t, nu)
# Convex combination of the two pushforwards
interpolate = (1 - t) * rho_fwd + t * rho_bwd
# Plot the interpolation
ax[i].imshow(interpolate, origin='lower', extent=(0, 1, 0, 1), vmax=vmax)
ax[i].set_title(f"$t={t:.2f}$")
# Adjust the main subplot layout to leave room for a dedicated colorbar axis
plt.subplots_adjust(right=0.85) # Shrink subplots to make room on the right
# Create a new axis for the colorbar (position: [left, bottom, width, height])
cbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.88, 0.15, 0.03, 0.7])
fig.colorbar(im0, cax=cbar_ax, label='Intensity')
plt.show()
plot_interpolation(mu, nu, phi, psi, bf, x, y)
plt.show()